
A beehive isn't as complicated as it seems, once you see it in action! Honey bees live in large groups of 30,000 to 60,000 bees called a colony. In nature, this would often be a hollow tree.
 Beekeepers supply wooden hives to house the colony. The interior
of these hives include wax combs (sheets of 6-sided cells) that the
bees will use to make and store honey. Combs are also used to store
pollen and as nurseries for bee larvae. The combs are built
vertically, side by side. Thousands of cells make up each
comb. The bees produce wax by secreting it in small flakes from the
underside of the worker bees’ abdomens. The bees then chew the wax
to make it pliable and build one or more combs.
Beekeepers supply wooden hives to house the colony. The interior
of these hives include wax combs (sheets of 6-sided cells) that the
bees will use to make and store honey. Combs are also used to store
pollen and as nurseries for bee larvae. The combs are built
vertically, side by side. Thousands of cells make up each
comb. The bees produce wax by secreting it in small flakes from the
underside of the worker bees’ abdomens. The bees then chew the wax
to make it pliable and build one or more combs.
There are generally two sizes of cells within the hive. Most of
the cells, measuring approximately 0.20 inches across, are used for
raising worker bees. Slightly larger cells, about 0.25 inches
across, are used for rearing
drones. Both kinds of cells are used
for storing pollen and honey. Cells in the middle part of the comb
are generally used as the nursery. This helps to protect the young
developing bees from changes in weather and
other dangers.
Nursery cells are used over and over again. Worker bees clean each cell carefully before the queen lays another egg inside. Pollen is stored close to the nursery area in order to feed young bees. The outer portion of the comb is used for honey storage.
Beehive Glossary
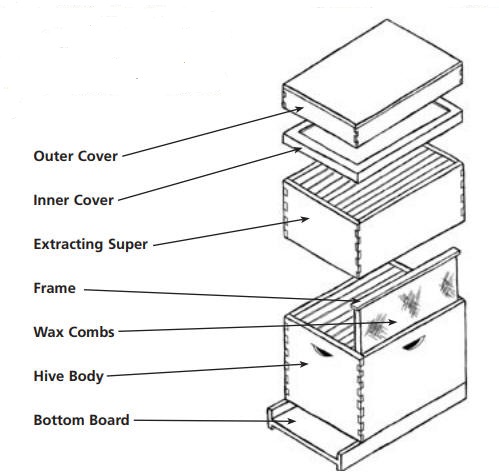
Bottom board - wooden stand on which the hive rests. Set bottom board on bricks or concrete blocks to keep it off the ground.
Brood cells - cells that house developing bees.
Cell - a hexagonal wax chamber built at a slight upward angle by honey bees for brood rearing and storing pollen and honey.
Colony - a group of animals living together.
Comb - a structure made up of hexagonal wax cells.
Extracting Super - the area of trays of combs that will be removed to extract the honey,
Frames and foundation - wooden frames that hold sheets of beeswax foundation and are imprinted with the shapes of hexagonal cells. Bees use the foundation to build straight combs.
Hive - a home to a colony of bees. It is a large wooden box (called a "super") that holds 10 frames of comb.
Hive body or brood chamber - laThis space (the brood nest) is reserved for the bees to rear brood and store honey for their own use. Either one or two hive bodies can be used for a brood nest. Two hive bodies are common in cold winter regions. Beekeepers in areas with mild winters successfully use only one hive body.
Inner cover - prevents bees from attaching comb to outer cover and provides insulating dead air space.
Outer cover - provides weather protection.
Propolis - a sticky substance collected from trees by bees and used as glue to construct and seal parts in the beehive and protect the hive from the elements.
Queen excluder - placed between the brood nest and the honey supers. This device keeps the queen in the brood nest, so brood will not occur in honey supers. An excluder is usually not necessary if two hive bodies are used.
Wax - the substance excreted from the glands located on the underside of a honey bee between its abdominal segments.
Vertical wax combs - the area that is left alone for the honey bees to raise their young and store pollen and honey that they need to live on.
Other Beekeeping tools
- Smoker - Produces smke that calms bees and reduces stinging. Pine straw, grass and burlap make good smoker fuel.
- Hive tool - Used for for prying apart supers and frames.
- Veil and gloves - Protects the beekeeper's head and arms from stings. Experienced beekeepers often prefer to work without gloves.
- Feeders - This holds the simple sugar syrup that is fed to bees in early spring and in fall, when their own supplies of honey are low and there aren't many flowers to visit