A standard jar of honey from the supermarket requires bees to make a million flower visits. A colony might produce 50 to 100 such jars per year.
Honey Facts
- Honey has antibacterial properties; particularly Manuka and Tualang honeys from New Zealand
- Honey is 80% sugars and 20% water.
- Honey is the only food source produced by an insect that humans eat.
- Bees produce many things that directly benefit humans, such as honey, wax, resins, propolis, royal jelly.
- Honey never spoils. (if it crystalizes, just heat it gently until it liquefies again)
- The top honey-producing states are California, Florida, and South Dakota.
- Honey is mentioned in the Bible: "My son, eat thou honey, because it is good; and the honeycomb, which is sweet to thy taste." Proverbs 24:13
Economic impact
- There are an estimated 3.2 million honey bee colonies are in the United States.
- There over 200,000 beekeepers maintain honey bee colonies within the United States.
- South Dakota, North Dakota, Florida and California are known as the biggest honey-producing states.
- Honey bees contribute over $14 billion to the value of U.S. crop production.
- Honey bees pollinate $2.5 billion of California's almond production.
- Honey bees produce $150 million worth of honey and beeswax in the US.
Honeybee Facts
Overall facts
- There are over 25,000 species of bees.
- Each honey bee produces about 1/12 of a teaspoon of honey.
- An average hive can produce over 200 pounds per hive. However, this reduces as you move into hotter climates. For example in the Atlanta area, a hive typically produces about 60-100lbs.
- There were no honey bees in America before European settlers brought hives from Europe.
- Out of 20,000 species of bees, only 4 make honey.
Bee physiology and Bee lives
- Honey bees fly at 15 miles per hour.
- A honeybee's wings flap over 183 times per second or 11,400 times per minute,
- It would take about 1 ounce of honey to fuel a honeybee's flight around the world (about 25,000 miles per ounce).
- Bees have an excellent sense of smell.
- Honeybees are the only bees that die after they sting.
- Honeybees have five eyes, 3 small ones on top of the head and two big ones in front. They also have hair on their eyes!
- Worker bees suck up flower nectar and store it in a special honey stomach to regurgitate back at the hive into a cell.
- Natural chemicals from the bee's head glands combined with the evaporation of the water from the nectar changes the nectar into honey.
- Honeybees never sleep!
- An worker bee's lifespan is about 45 days from the day the energy from the pupa stage. In cooler areas, like Northern parts of US and Canada or over the winter, they can live up to 5 months.
- The most common cause of death for a honey bee is their wings wear out.
- During their short lives the average worker bee produces 1/12 of a teaspoon of honey
- A typical beehive can make up to 400 pounds of honey per
year.
- Bees can be attacked by some mites, particularly the Varroa Mite. To treat this, beekeepers use formic acid (the same natural acid that ants produce to mark their trails) . This is an organic approved miticide.
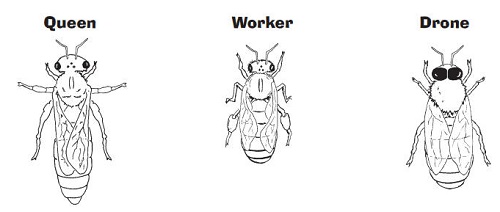
Queens, Workers, Drones and more
- Hives have 3 "genders" of bees: Queens, Workers and Drones. The workers are further specialized into Nurses, Guards, etc.
- A queen bee can sting multiple times without dying.
- A queen can lay up to 3,000 eggs per day.
- Female bees are called "worker bees" and they collect the nectar, pollen and do all the work of maintaining the hive.
- Worker honey bees transform the floral nectar the gather into honey by adding enzymes to the nectar and reducing the moisture.
- Male bees ("drones") do not have stingers.
- A drone's only purpose is to mate with the queen bee.
-
Royal jelly is a special type of honey that’s high in nutrients
that is fed to a few larvae and turns the larva into a queen.

- 99% of the bee colony is made up of worker bees.
- Bees positions themselves around the hive and at the openings to flap their wings to maintain a temperature of 92-93 degrees Fahrenheit regardless of the outside temperature.
- California, Georgia, and Texas are the top 3 states in producing honey bees and queen bees for sale?
Bees Colonies and hives
- A typical Bee colony consists of 30,000 to 60,000 bees.
- A single colony brings in about 250 pounds of nectar per year
- Honeycomb cells are made of a wax that the bees make.

- Each cell is a hexagon, with 6 sides
- Bees can overwhelm intruders by stinging them to death, biting them apart or if that fails, swarming over the intruder until it either suffocates for dies from overheating
- Beekeepers use smoke to mask the bee's alarm pheromone. Since the bees think there is a fire is near their hive, they try to save the hive by eating the honet which they can later reguritate in a new hive. And it just happens that when they are stuffed with honey, it is difficult for them to sting.
Pollination
- Bees pollinate over 130 fruit and vegetable crops.
- Honey bees pollinate 1/3 of the human diet.
- Honey bees pollinate 50 different US crops valued at over $20 billion.
- The honeybee does not know how to pollinate tomato or eggplant flowers. It does very poorly compared to native bees when pollinating many native plants, such as pumpkins, cherries, blueberries, and cranberries.
- Honeybees will usually travel approximately 3 miles from their hive.
- Honeybees are responsible for pollinating approx. 80% of all fruit, vegetable and seed crops in the U.S.
- A single honey bee will visit 50-100 flowers on a single trip out of the hive.
- Bees must visit 2 million flowers in order to produce 1 pound of honey.
- Honey Bees do a dance in flight when they return to the hive that instructs the other bees where the flowers are.
- To make one pound of honey, the bees in the colony must visit 2 million flowers, fly over 55,000 miles and will be the lifetime work of approximately 768 bees.