
Everything Your Wanted To Know About Honey
Honey is essentially a highly concentrated water solution of two sugars, fructose and glucose, with small amounts of at least 22 other more complex sugars. Many other substances also occur in honey, but the sugars are by far the major components. Honey provides 64 calories in a serving of one tablespoon (15 ml) equivalent to 1272 kJ per 100 g.
Composition of honey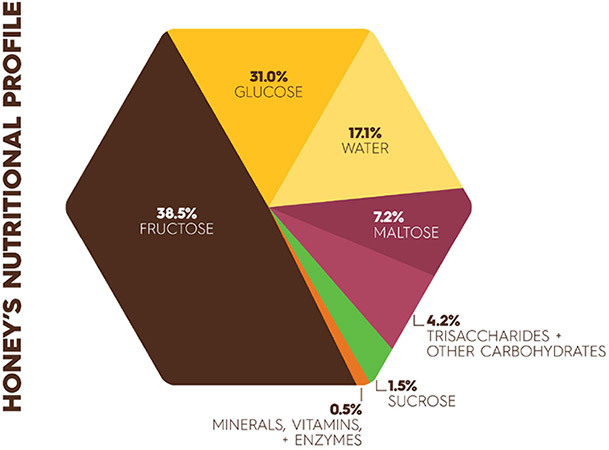
Mixed floral honey from several United States regions typically contains:
- Fructose: 38.2%
- Glucose: 31.3%
- Maltose: 7.1%
- Sucrose: 1.3%
- Water: 17.2% (Honey is ripe when capped with a thin layer of wax by honey bees at about 18.6% moisture (water).
- Higher sugars: 1.5%
- Ash: 0.2%
- Other/undetermined: 3.2%
We can see that this can vary considerably, and globally. A 2013 study of 20 different honeys from Germany found:
- Fructose: 28% to 41%
- Glucose: 22% to 35%
So, honey is composed primarily of fructose and glucose but also contains fructo-oligosaccharides (1) .Sugar accounts for 95-99% of honey dry matter.
Honey also contains many amino acids, vitamins, minerals and enzymes (2). The composition of honey varies depending on the plants on which the bees forage. Almost all natural honey contains flavonoides (such as apigenin, pinocembrin, kaempferol, quercetin, galangin, chrysin and hesperetin), phenolic acids (such as ellagic, caffeic, p-coumaric and ferulic acids), ascorbic acid, tocopherols, catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), reduced glutathione (GSH), Millard reaction products and peptides.
Color
The color in liquid honey varies from clear and colorless (like water) to dark amber or black. The various honey colors are basically all shades of yellow and amber. Color varies with botanical origin, age, and storage conditions, but transparency or clarity depends on the amount of suspended particles such as pollen (24). Less common honey colors are bright yellow (sunflower), reddish undertones (chest nut), grayish (eucalyptus) and greenish (honeydew).
Crystallization of Honey
Honey crystallization results from the formation of monohydrate
glucose crystals, which vary in number, shape, dimension, and
quality with the honey composition and storage conditions. The lower
the water and the higher the glucose content of honey, the faster
the crystallization. Once crystallized, honey turns lighter in color
because the glucose crystals are white.
See this page for much more about honey
crystallization and how to return it to a liquid state!
Honey is not for infants!
Never Give Honey to an Infant, under 1 year old. Botulism
bacteria are present in honey naturally, and while this is
harmless to adults, and children over 1 year old, Infants do not
have a developed immune system to defend against infection. And
although it is extremely rare, the infection can cause a paralytic
disorder in which the infant must be given anti-toxins and often be
placed on a respirator in an intensive care unit,
Cereals that
contain honey are ok because they are cooked.
Health and Medical Benefits of Honey
Honey has been reported to have an inhibitory effect on around 60 species of bacteria, some species of fungi and viruses. See this page for an examination of medical benefits to honey.
Antioxidant capacity of honey is another positive effect of honey consumption, along with helping in reducing symptoms of local allergens. See this page for more information.
| Nutrient Unit | Value units | per cup (339 g) | per tbsp (21 g) | per tbsp (21 g) | per packet (0.5 oz) ( or 14 g) |
| Water | g | 17.10 | 57.97 | 3.59 | 2.39 |
| Energy | kcal | 304 | 1031 | 64 | 43 |
| Protein | g | 0.30 | 1.02 | 0.06 | 0.04 |
| Total lipid (fat) | g | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Carbohydrate, by difference | g | 82.40 | 279.34 | 17.30 | 11.54 |
| Fiber, total dietary | g | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Sugars, total | g | 82.12 | 278.39 | 17.25 | 11.50 |
| Minerals | |||||
| Calcium, Ca | mg | 6 | 20 | 1 | 1 |
| Iron, Fe | mg | 0.42 | 1.42 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Magnesium, Mg | mg | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Phosphorus, P | mg | 4 | 14 | 1 | 1 |
| Potassium, K | mg | 52 | 176 | 11 | 7 |
| Sodium, Na | mg | 4 | 14 | 1 | 1 |
| Zinc, Zn | mg | 0.22 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Vitamins | |||||
| Vitamin C, total ascorbic acid | mg | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Thiamin | mg | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Riboflavin | mg | 0.038 | 0.129 | 0.008 | 0.005 |
| Niacin | mg | 0.121 | 0.410 | 0.025 | 0.017 |
| Vitamin B-6 | mg | 0.024 | 0.081 | 0.005 | 0.003 |
| Folate, DFE | µg | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| Vitamin B-12 | µg | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Vitamin A, RAE | µg | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vitamin A, IU | IU | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) | mg | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Vitamin D (D2 + D3) | µg | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Vitamin D | IU | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Vitamin K (phylloquinone) | µg | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lipids | |||||
| Fatty acids, total saturated | g | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Fatty acids, total monounsaturated | g | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Fatty acids, total polyunsaturated | g | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Cholesterol | mg | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |